🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴🌴 🌴🌴🌴🌴
Introduction to Binary Tree Program in C (सी में बाइनरी ट्री कार्यक्रम का परिचय)
Binary tree program in C is a nonlinear data structure used for data search and organization. Binary tree is comprised of nodes, and these nodes each being a data component, have left and right child nodes. Unlike other data structures, such as, Arrays, Stack and queue, Linked List which are Linear type data structures whereas Trees are Hierarchical type of data structures. Binary search tree or BST in short, whose nodes each store keys greater than their left child nodes and less than all the right child nodes. As the data in a binary tree is organized, it allows operations like insertion, deletion, update and fetch. Let us dive deeper into the concepts related to the Binary tree and implement some of the examples using C programming language.
(सी में बाइनरी ट्री प्रोग्राम डेटा खोज और संगठन के लिए उपयोग किया जाने वाला एक गैर-लाइनियर डेटा संरचना है। बाइनरी ट्री में नोड्स शामिल होते हैं, और ये नोड्स प्रत्येक डेटा घटक होने के नाते, बाएं और दाएं बच्चे के नोड्स होते हैं। अन्य डेटा संरचनाओं के विपरीत, जैसे, सरेर, स्टैक और कतार, लिंक्ड सूची जो रैखिक प्रकार की डेटा संरचनाएं हैं जबकि पेड़ पदानुक्रमित प्रकार की डेटा संरचनाएं हैं। बाइनरी खोज पेड़ या बीएसटी संक्षेप में, जिनकी नोड्स प्रत्येक स्टोर चाबियाँ उनके बाएं बच्चे नोड्स से अधिक और सभी दाहिने बच्चे नोड्स से कम हैं। एक बाइनरी पेड़ में डेटा का आयोजन किया जाता है के रूप में, यह प्रविष्टि, हटाने, अद्यतन और लाने की तरह आपरेशनों की अनुमति देता है । आइए हम बाइनरी ट्री से संबंधित अवधारणाओं में गहराई से गोता लगाएं और सी प्रोग्रामिंग भाषा का उपयोग करके कुछ उदाहरणों को लागू करें।)
👉सिनकर Syntax:-
बाइनरी ट्री में कोई विशेष वाक्य विन्यास नहीं है, लेकिन बाइनरी ट्री को लागू करने में पालन करने के लिए एक एल्गोरिदम है।
(Binary tree does not have any particular Syntax but has an Algorithm to follow in implementing Binary Tree.)
struct BT {
int data;
struct BT *rightNode, *leftNode;
};
- नोड के बाएं उप वृक्ष में नोड की चाबी से कम चाबियों के साथ नोड्स होते हैं
- नोड के दाहिने उप वृक्ष में नोड की कुंजी से अधिक चाबियों के साथ नोड्स होते हैं
- बाएं और दाएं दोनों उप वृक्ष भी बाइनरी ट्री होना चाहिए, और किसी भी डुप्लिकेट की अनुमति नहीं है।
- Left sub tree of node contains nodes with keys less than node’s key
- Right sub tree of node contains nodes with keys greater than node’s key
- Both left and right sub tree must also be a Binary tree, and no duplicates are allowed.
👉Illustration of Binary Tree (बाइनरी ट्री का चित्रण)
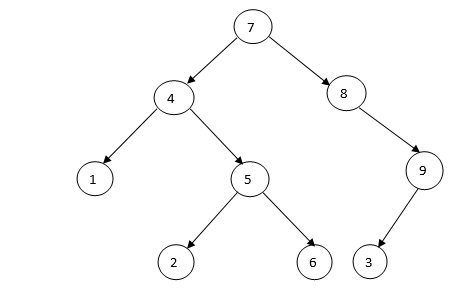
Above properties of Binary tree provide ordering among keys such that operations like search, min, and max can be done faster. If in case there is no order, then user has to compare every key for searching a given key.
बाइनरी ट्री के ऊपर गुण चाबियों के बीच ऑर्डर प्रदान करते हैं जैसे कि खोज, न्यूनतम और अधिकतम जैसे ऑपरेशन तेजी से किए जा सकते हैं। यदि कोई आदेश नहीं है, तो उपयोगकर्ता को दी गई कुंजी खोजने के लिए हर कुंजी की तुलना करनी होती है।
👉 बाइनरी ट्री के लिएएल्गोरिदम Algorithm for Binary Tree
1. A new binary tree is created and values are assigned
2. Write a function insert() in such a way that node and key will be two parameters and check for below conditions,
a. If rootNode == NULL, then return new node to calling function.
b. If rootNode => data < keyValue, then call insert() with rootNode => rightNode and assign return value in rootNode => rightNode.
c. If rootNode => data > keyValue, then call insert() with rootNode => leftNode and assign return value in rootNode => leftNode
3. Then finally, we can return original rootNode pointer to calling function.
Example #1: C program for insertion in a Binary tree
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct BTnode
{
int keyVal;
struct BTnode *leftNode;
struct BTnode *rightNode;
};
struct BTnode *getNode(int value)
{
struct BTnode *newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BTnode));
newNode->keyVal = value;
newNode->leftNode = NULL;
newNode->rightNode = NULL;
return newNode;
}
struct BTnode *insert(struct BTnode *rootNode, int value)
{
if(rootNode == NULL)
return getNode(value);
if(rootNode->keyVal < value)
rootNode->rightNode = insert(rootNode->rightNode,value);
else if(rootNode->keyVal > value)
rootNode->leftNode = insert(rootNode->leftNode,value);
return rootNode;
}
void insertorder(struct BTnode *rootNode)
{
if(rootNode == NULL)
return;
insertorder(rootNode->leftNode);
printf("%d ",rootNode->keyVal);
insertorder(rootNode->rightNode);
}
int main()
{
struct BTnode *rootNode = NULL;
rootNode = insert(rootNode,7);
rootNode = insert(rootNode,4);
rootNode = insert(rootNode,8);
rootNode = insert(rootNode,1);
rootNode = insert(rootNode,5);
rootNode = insert(rootNode,2);
rootNode = insert(rootNode,9);
rootNode = insert(rootNode,3);
insertorder(rootNode);
return 0;
}
![]()
So here we are creating a Binary tree and then inserting the node values (तो यहां हम एक बाइनरी पेड़ बना रहे हैं और फिर नोड मूल्यों को सम्मिलित कर रहे हैं.)
Example #2: Binary tree, inorder, preorder, and postorder traversal in C programming.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct BTnode {
int data;
struct BTnode* leftNode;
struct BTnode* rightNode;
};
void inorder(struct BTnode* rootNode) {
if (rootNode == NULL) return;
inorder(rootNode->leftNode);
printf("%d ->", rootNode->data);
inorder(rootNode->rightNode);
}
void preorder(struct BTnode* rootNode) {
if (rootNode == NULL) return;
printf("%d ->", rootNode->data);
preorder(rootNode->leftNode);
preorder(rootNode->rightNode);
}
void postorder(struct BTnode* rootNode) {
if (rootNode == NULL) return;
postorder(rootNode->leftNode);
postorder(rootNode->rightNode);
printf("%d ->", rootNode->data);
}
struct BTnode* createNode(value) {
struct BTnode* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct BTnode));
newNode->data = value;
newNode->leftNode = NULL;
newNode->rightNode = NULL;
return newNode;
}
struct BTnode* insertLeftNode(struct BTnode* rootNode, int value) {
rootNode->leftNode = createNode(value);
return rootNode->leftNode;
}
struct BTnode* insertRightNode(struct BTnode* rootNode, int value) {
rootNode->rightNode = createNode(value);
return rootNode->rightNode;
}
int main() {
struct BTnode* rootNode = createNode(7);
insertLeftNode(rootNode, 4);
insertRightNode(rootNode, 8);
insertLeftNode(rootNode->leftNode, 1);
insertRightNode(rootNode->rightNode, 5);
insertLeftNode(rootNode->leftNode, 6);
insertRightNode(rootNode->rightNode, 3);
printf("Inorder \n");
inorder(rootNode);
printf("\nPreorder \n");
preorder(rootNode);
printf("\nPostorder \n");
postorder(rootNode);
}
Output:
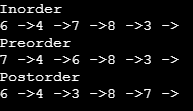
So here we have performed inorder, preorder, and postorder traversal for a Binary tree by inserting nodes.While searching for a value in Binary Tree, node is traversed from left to right.(तो यहां हमने नोड्स डालकर बाइनरी ट्री के लिए अक्रमक, प्रीऑर्डर और पोस्टऑर्डर ट्रैवर्सल किया है। बाइनरी ट्री में मूल्य की खोज करते समय, नोड बाएं से दाएं तक तय होता है।
👉Types of Binary Tree
पूर्ण बाइनरी ट्री (Full Binary Tree):-
बाइनरी ट्री के विशेष प्रकार जहां हर माता पिता नोड या एक आंतरिक नोड या तो 2 या कोई बच्चे नोड्स है ।Special type of Binary Tree where every parent node or an internal node has either 2 or no child nodes.
परफेक्ट बाइनरी ट्री(Perfect Binary Tree):-
एक बाइनरी ट्री जिसमें प्रत्येक आंतरिक नोड में बिल्कुल दो बच्चे होते हैं और सभी पत्ती एक ही स्तर पर नोड्स होती हैं। A Binary tree in which each internal node has exactly two children and all leaf nodes at same level.
पूरा बाइनरी ट्री Complete Binary Tree:-
यह पूर्ण बाइनरी ट्री के समान है, लेकिन सभी पत्ते नोड्स बाईं ओर होने चाहिए और हर स्तर पर बाएं और दाएं बच्चे दोनों नोड्स होने चाहिए। और आखिरी पत्ती के नोड में सही बच्चा नहीं होना चाहिए।
It is same as Full Binary Tree, but all leaf nodes must be at left and every level must have both left and right child nodes. And the last leaf node should not have the right child.
पैथोलॉजिकलट्री Pathological Tree:-
यह बाइनरी ट्री है जिसमें एक ही बच्चा है यानी या तो बाएं नोड या दाएं नोड. It is the Binary Tree having a single child i.e. either left node or right node
विषम बाइनरी ट्री Skewed Binary Tree:-
यह एक पैथोलॉजिकल पेड़ के समान है जिसमें बाइनरी पेड़ या तो बाएं या दाएं नोड्स का प्रभुत्व है। और इसके दो प्रकार होते हैं: बाएं विषम बाइनरी ट्री और दाएं विषम बाइनरी ट्री।
It is similar to a pathological tree in which the binary tree is either dominated by left or right nodes. And it has two types: Left Skewed Binary tree and Right Skewed Binary Tree.
संतुलित बाइनरी ट्री Balanced Binary Tree:-
बाइनरी ट्री का प्रकार जिसमें प्रत्येक बच्चे नोड के लिए बाएं और दाएं उपवृक्ष की ऊंचाई के बीच अंतर 0 या 1 है
Type of Binary Tree in which difference between the height of left and right subtree for each child node is 0 or 1
समाप्ति Conclusion
इसके साथ, हम अपने विषय "बाइनरी ट्री प्रोग्राम इन सी" को समाप्त करेंगे। हमने देखा है कि बाइनरी ट्री क्या है और इसका एल्गोरिदम। बाइनरी ट्री कैसे बनाया जाता है, सम्मिलन कैसे किया जाता है, और हम बाइनरी ट्री नोड्स और डिस्प्ले को कैसे खोज सकते हैं, इस पर कुछ उदाहरण देखे गए। बाइनरी ट्री के प्रकार भी हैं जिन्हें हमने ऊपर समझाया है। अन्य ऑपरेशन भी हैं, जो हमें बाइनरी ट्री की अवधारणा को पूरी तरह से समझने में मदद कर सकते हैं।
With this, we shall conclude our topic “Binary Tree program in C”. We have seen what Binary tree is and its Algorithm. Seen few examples on How Binary tree is created, how insertion is done, and how we can search the Binary Tree nodes and display. There are also types of Binary Tree which we have explained above. There are other operations too, which can help us to understand the concept of Binary Tree completely.
अनुशंसित लेख Recommended Articles
यह सी में बाइनरी ट्री कार्यक्रम के लिए एक गाइड है। यहां हम कोड कार्यान्वयन के साथ उदाहरणों के साथ परिचय, वाक्य रचना, बाइनरी ट्री के प्रकारों पर चर्चा करते हैं। आप और अधिक जानने के लिए निम्नलिखित लेखों पर भी एक नज़र डाल सकते हैं -
This is a guide to Binary Tree Program in C. Here we discuss the Introduction, syntax, Types of Binary Tree with Examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –













2 Comments
good information about you
ReplyDeleteValuable content
ReplyDelete